What is SEL?
What is SEL?
31-Jan-2022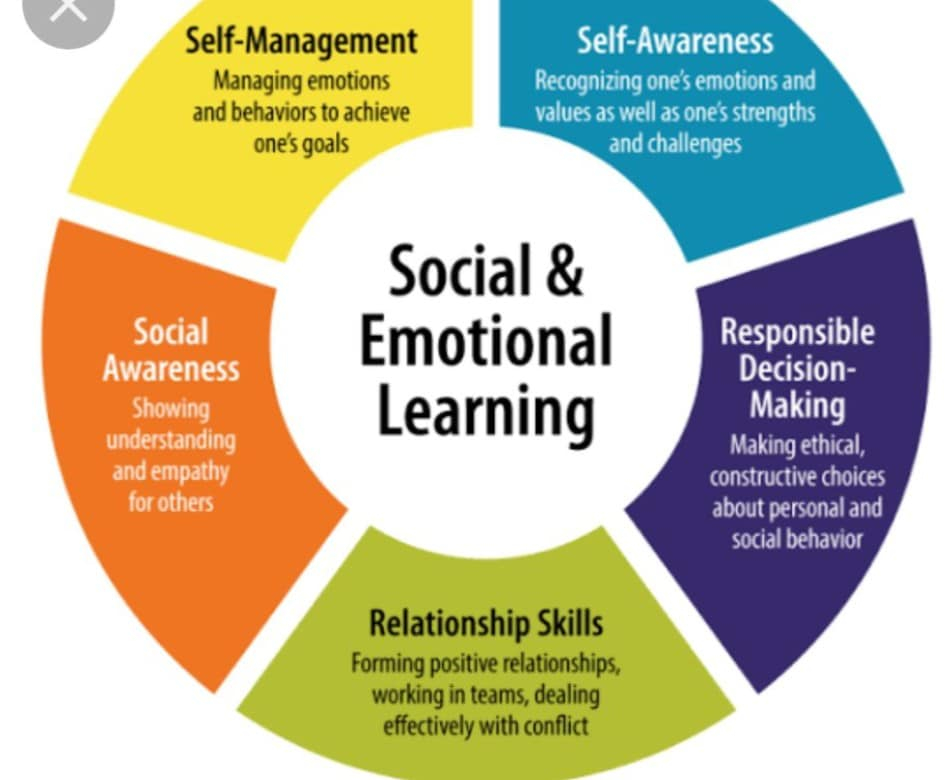
Social-emotional learning, commonly referred to by its acronym, SEL, is a method of promoting holistic child development by teaching students skills such as self-regulation, persistence, empathy, self-awareness, and mindfulness.
Why are schools teaching social-emotional learning?
Social-emotional learning has practical benefits for the classroom by teaching students to regulate their emotions, pay attention, and work well with their peers. But it does a lot more than that: SEL has been shown to boost students’ test scores and grades, promote on-time graduation and college enrollment, increase students’ financial earnings as adults, and support their mental and physical well-being.
What specific skills should students learn?
SEL researchers and leaders agree on three areas:
Cognitive — Executive-function skills that help students manage themselves by regulating their own behavior, paying attention, remembering lessons, and organizing tasks.
Social — Skills that help students get along with others by teaching compassion, collaboration, communication, listening, conflict resolution, and social cue recognition.
Emotional — Skills that help students manage feelings like anger, frustration, and sadness, and teach them to recognize these emotions in others.
The 5 Core SEL Competencies:
1. Self-Awareness.
2. Self-Management.
3. Social Awareness.
4. Relationship Skills.
5. Responsible Decision-Making.
What are the three pillars of social and emotional learning?
Three Pillars: Culture, Adult Skills, Curriculum. A culture where social emotional learning can thrive is one that provides a safe and healthy place for children to learn and grow.
Why is social and emotional learning important?
SEL can help students better understand and identify their emotions; it can help them develop empathy, increase self-control and manage stress. It also helps them build better relationships and interpersonal skills that will serve them in school and beyond, helping them succeed as adults.
More Blog
Mental health needs to notice in Bangladesh
12-Sep-2024Like other countries Mental health is one of the warning issues in Bangladesh gradually. Though the immense consequences of this... read more
Happiness tips:
02-Apr-2022Happiness is also one of the important aspects of positive psychology and wellbeing. Do something you enjoy every day, e... read more
What is SEL?
31-Jan-2022Social-emotional learning, commonly referred to by its acronym, SEL, is a method of promoting holistic child development by teac... read more


